SASE Secure Connect: A Practical Guide for Modern Networking
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the fundamentals of Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) and its role in modern networking.
- Exploring the benefits of integrating SASE into your organization’s network infrastructure.
- Identifying best practices for implementing SASE to enhance security and performance.
Introduction to SASE
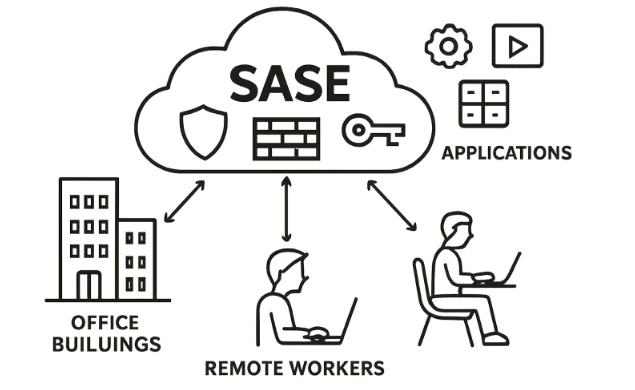
As digital transformation and the widespread adoption of cloud applications continue to reshape how organizations operate, network security paradigms are evolving to support a distributed, mobile workforce. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) is the answer for businesses seeking to effectively converge comprehensive networking and security functions into a unified, cloud-native framework. Trusted SASE solutions are helping organizations streamline secure connectivity for users, devices, and applications—regardless of location.
SASE’s cloud-delivered architecture eliminates the complexity of patchwork legacy systems, replacing hardware-focused networks with agile, software-driven protection. This offers a centralized, policy-driven approach to safeguarding data, simplifying management, and improving visibility—all while supporting the scalability requirements of modern enterprises. By integrating threat prevention, secure web gateways, and zero-trust network access, SASE ensures consistent enforcement of security policies across all users and endpoints. The platform’s adaptability allows businesses to respond quickly to emerging risks, reducing potential attack surfaces and minimizing downtime. With built-in analytics and monitoring, organizations gain actionable insights to manage vulnerabilities and optimize network performance proactively. As a result, SASE strengthens security posture and enhances operational efficiency, making it a strategic investment for future-ready IT infrastructure.
- Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN): This type of network provides intelligent traffic management across multiple WAN connections, improving application reliability and efficiency.
- Secure Web Gateway (SWG): Inspects web traffic at the cloud’s edge to block malicious content, enforce usage policies, and prevent data leakage.
- Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB): This broker offers visibility, compliance controls, and security policy enforcement for cloud applications and services.
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA): Approaches access with the philosophy of “never trust, always verify,” checking user identity, device health, and context before granting resources.
- Firewall as a Service (FWaaS): Centralizes advanced firewall functionalities in the cloud, reducing deployment overhead and offering granular, real-time threat defense.
This confluence of tools and services enables organizations to establish a resilient security perimeter that follows users and devices, regardless of physical location.
Benefits of Adopting SASE
The shift towards SASE delivers transformative benefits that align with business goals and security priorities:
- Unprecedented Security: The integrated approach ensures organizations can apply uniform security policies across the network, reducing exposure to threats and data breaches.
- Operational Efficiency: Centralizing management reduces complexity and maintenance overhead while improving visibility.
- Better User Experience: Intelligent routing and edge-based security services minimize latency, improving application responsiveness for end users.
- Agility and Scalability: With cloud-first architecture, businesses can easily scale network and security resources in response to changing demands.
- Cost Optimization: Consolidating disparate security appliances into a single platform lowers hardware investments and operating costs.
Implementing SASE in Your Organization
Successful SASE adoption involves the integration of advanced security and networking technologies with minimal business disruption. Key steps include:
- Assess Existing Infrastructure: Map out current tools and workflows to identify operational inefficiencies and security gaps.
- Clarify Security Policies: Set clear, enforceable security guidelines that reflect regulatory requirements and business needs.
- Choose the Right Vendor: Evaluate providers based on their ability to deliver end-to-end SASE capabilities and their reputation for customer support.
- Strategic Integration: Collaborate with cross-functional teams to outline integration steps and minimize impact on daily operations.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Optimization: Use real-time analytics and feedback to fine-tune configurations, ensuring the solution continues to meet performance and security objectives.
Best Practices for SASE Deployment
- Embrace Zero Trust: Move away from implicit trust by rigorously validating identities and inspecting all network traffic.
- Maximize Visibility: Deploy solutions that offer granular monitoring and reporting, providing IT and security teams actionable insights.
- User-Centric Design: Optimize security and network paths for fast, reliable end-user experiences—particularly for remote and mobile workers.
- Stakeholder Alignment: Engage leadership and end-users early to ensure requirements and expectations align with technical capabilities.
Challenges and Solutions in SASE Adoption
Transitioning to SASE may raise hurdles. Integration can be technically complex, especially when aligning new tools with entrenched legacy systems. Organizations often face a shortage of in-house expertise for SASE’s evolving technologies; investing in targeted staff training can bridge this gap. Change management is equally critical: effective stakeholder communication, phased rollouts, and ongoing support help drive user buy-in and minimize disruption.
- Integration Complexity: Partner with experienced SASE vendors and plan integrations in phases.
- Skill Gaps: Provide ongoing education and hands-on training sessions for IT staff.
- Managing Change: Transparently communicate the vision and advantages of SASE to internal stakeholders throughout the transition.
Future Trends in SASE and Network Security
The SASE market is evolving quickly. Emerging trends include greater reliance on artificial intelligence for predictive threat analytics and deeper, automatic integrations with identity management and endpoint security tools. The focus is shifting toward delivering intuitive, seamless experiences for users without sacrificing vigilance against threats. As data privacy regulations proliferate and remote work persists, organizations will increasingly view SASE as vital to future-proofing their digital frameworks and ensuring compliance moving forward. Organizations also prioritize scalability, seeking SASE solutions that can grow with business demands while maintaining consistent security policies across all locations. Cloud-native architectures are becoming the norm, allowing for faster deployment and simplified distributed network management. Vendors invest heavily in unified dashboards that provide real-time visibility and actionable insights, reducing the complexity traditionally associated with multiple security tools. Collaboration between security teams and network operations is improving as SASE platforms enable centralized policy enforcement without slowing down performance. Ultimately, the evolution of SASE is positioning it as a cornerstone of resilient, adaptive, and user-centric cybersecurity strategies for modern enterprises.

Samar
Punsuniverse — a realm crafted by me, Samar! You will find everything here that is related to puns, weather its food, animals, names or something elsse.






